plant based nanoparticles
The thermal conductivity of silver and even oxides like zinc oxide is more than that of engine oil and water at room temperature 74. Experiments on plant-derived approaches of bimetallic nanoparticles have helped describe novel passages for the production of ranging sizes and morphological shapes of NPs such as cube rhombic dodecahedron tetrahedron octahedron and spherical irregular and crystal-shaped nanomaterials 22.
Molecules Free Full Text Green Silver And Gold Nanoparticles Biological Synthesis Approaches And Potentials For Biomedical Applications Html
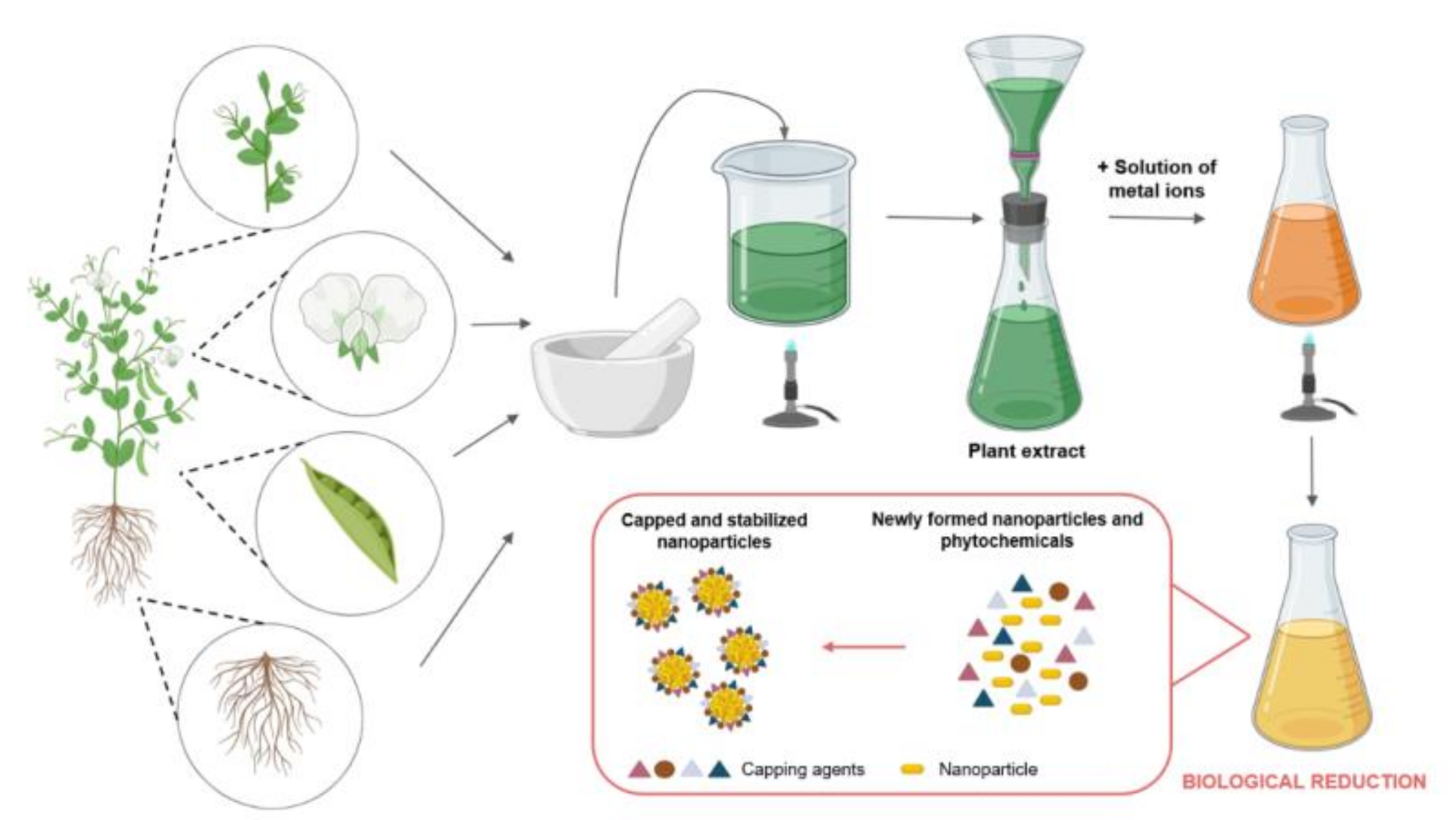
Plant-Based Green Synthesis of Nanoparticles.
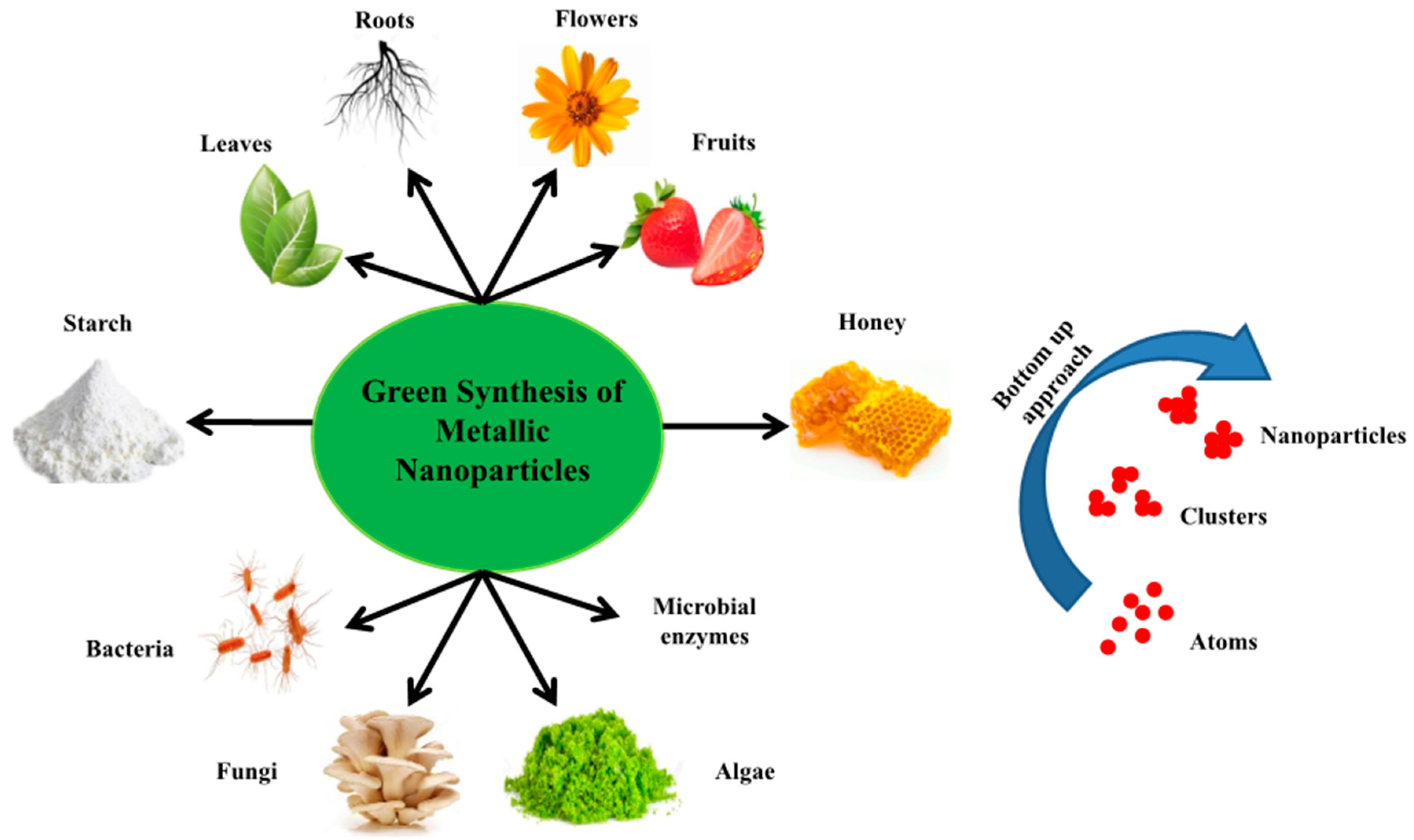
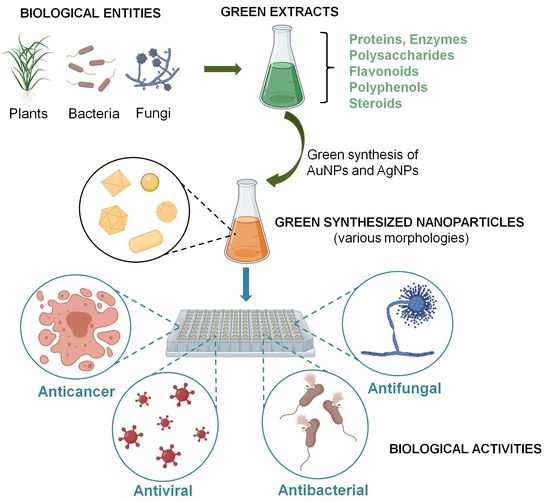
. Biosynthesized Nanoparticles in Cancer Metals and Metal Oxides The plant-based green synthesis of metal and metal oxide NPs has gained great attention due to their non-toxic non-hazardous cost-effective and eco-friendly properties. Thus they are suitable for large-scale biosynthesis of nanoparticles. A using microorganisms such as fungi yeasts eukaryotes bacteria and actinomycetes prokaryotes b using plants and plant extracts and c the use of membranes viruss DNA and diatoms.
In phyto-formulation studies researchers have attempted to develop nano-dosage forms such as liposomes proliposomes solid lipid nanoparticles NPs nanoemulsion and protein-based and lipid-based drug delivery systems. The study of cytotoxic and genotoxic impacts of silver nanoparticles below 100 nm size using root tip cells of Allium cepa shows that higher. Recently biological nanoparticles were found to be more pharmacologically active than physicochemically synthesized nanoparticles.
Metal nanoparticles produced using microorganisms and plant extracts are stable and can be monodispersed by controlling synthetic parameters such as pH temperature incubation period and mixing ratio. Biogenic Pd-based NPs from plant extracts have been identified as valuable nanocatalysts in various catalytic reactions because of their excellent activities and selectivity. It is evident from the earlier reports that plants are the better candidates for synthesis of nanoparticles as nanoparticles produced by using plants parts are more stable and also the rate of synthesis is faster than in the case of microorganisms Iravani 2011.
In this review we focused the green synthesis of AgNPs using plant extract. FTIR is a highly reliable analytical method that detects and displays. XRD is a characterization methodology for measuring the crystallinity of the AgNPs.
They are non-toxic have tissue-specific targeting properties and can be mass-produced. Among the metal nanoparticles gold nanoparticles are recognized as the most potent biocompatible and environment-friendly. I first of all reduction in metal ions takes place by the phytoconstituents followed by nucleation of reduced metal atoms that is called activation phase.
Thus they have great potential for clinical applications. IC50 410 μgmL on human embryonic kidney cells HEK 293 was measured. Iii termination is the last phase during which NPs attain their.
PDNPs off Recent Review Articles. It is well recognizing statement that plant-based metallic nanoparticles have thermal conductivity more than solutions in hard form. Production Characterization and Applications.
Characterization of plant-based silver nanoparticles- X-Ray diffraction XRD. General mechanism involved in plant-based NP formation is proposed as. Fourier transform infrared FTIR spectroscopy.
In this section the toxicity of various nanoparticles with plant-based green synthesis both in vitro and in vivo studies are deliberated. Starch nanoparticles were synthesized using nanoprecipitation without microemulsion method by the addition of 1mL of the starch solution to 20 mL of absolute ethanol with continuous stirring at various stirring rates such as 300 600 and 900 rpm for 1 h. Plant-derived edible nanoparticles PDNPs are nano-sized membrane vesicles released by edible plants such as grapefruit ginger broccoli and lemon.
Besides obtained NPs are more bio-compatible than chemical synthesized ones. Nanomaterials have revolutionized the world of cancer therapy and plant-derived nanoparticles have the added advantage of being cost-effective and easy to mass produce. Plant-Based Nanoparticles Could Eventually Replace Some Antibiotics Many researchers reported the adverse effect of nanoparticles on plant function some of which are discussed below.
A team of researchers from Immanuel Kant Baltic Federal University obtained magnetic nanoparticles using sweet flag Acorus calamus. Green synthesis of gold nanoparticles Gold NPs have been synthesized using different green approaches that include biologically based chemicals plantsplant-derived materials algae bacteria and microbes. The toxicity effect of plant-derived copper NPs on various animal cell lines has been investigated as exemplified by the study of Kumari P et al.
In this context plant-based nanoparticles will be. Both the roots and the leaves of this plant have antioxidant. The green-synthesized Au NPs have similar physical characteristics as chemically synthesized nanomaterials Table 2.
Ii during growth phase small NPs adhere to form large size NP Ostwald ripening. Owing to its safety both environmental and in vivo as well as the ease of synthesis biogenic routes especially the plant-based synthesis of metal nanoparticles has been preferred as the best strategy. The source of green synthesis can be categorized into three categories.
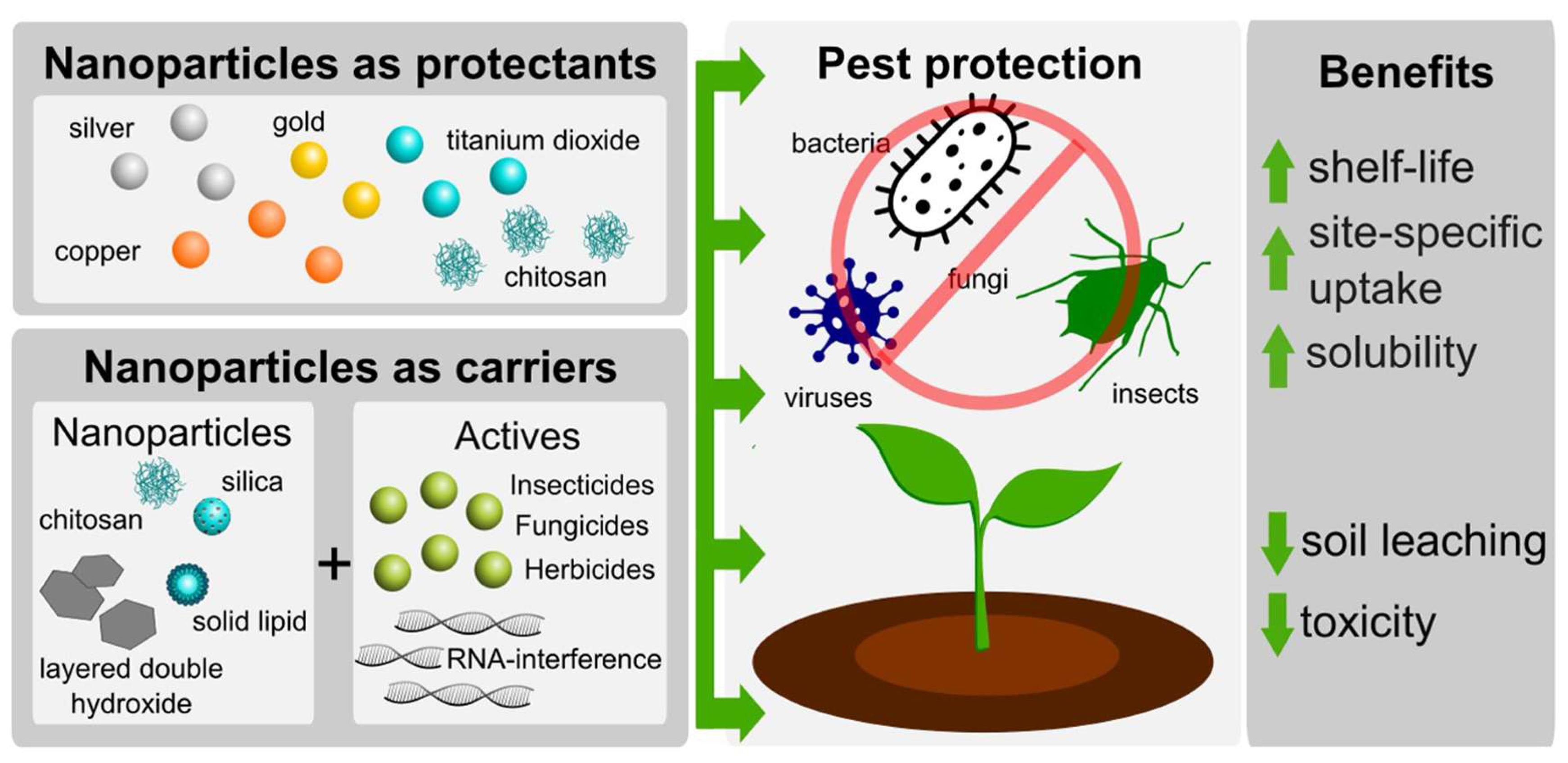
They have captured the attention of researchers owing to their economical sustainable green and eco-friendly nature. Nanotechnology is a fast-expanding and multidisciplinary field with many applications in science and technology. Multiple nanoparticle-based approaches to counter bacterial infections providing crucial insight into the design of elements that play critical roles in the creation of antimicrobial nanotherapeutic drugs are currently underway.
Researchers from Tokyo. Herbal medicines plant products and phytotherapeutics have been widely used all over the world since the ancient time.
Agronomy Free Full Text Nanotechnology For Plant Disease Management Html

Plant Extract Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles An Ongoing Source Of Novel Biocompatible Materials Sciencedirect

Nanomaterials Free Full Text Flower Based Green Synthesis Of Metallic Nanoparticles Applications Beyond Fragrance Html
Molecules Free Full Text Green Silver And Gold Nanoparticles Biological Synthesis Approaches And Potentials For Biomedical Applications Html
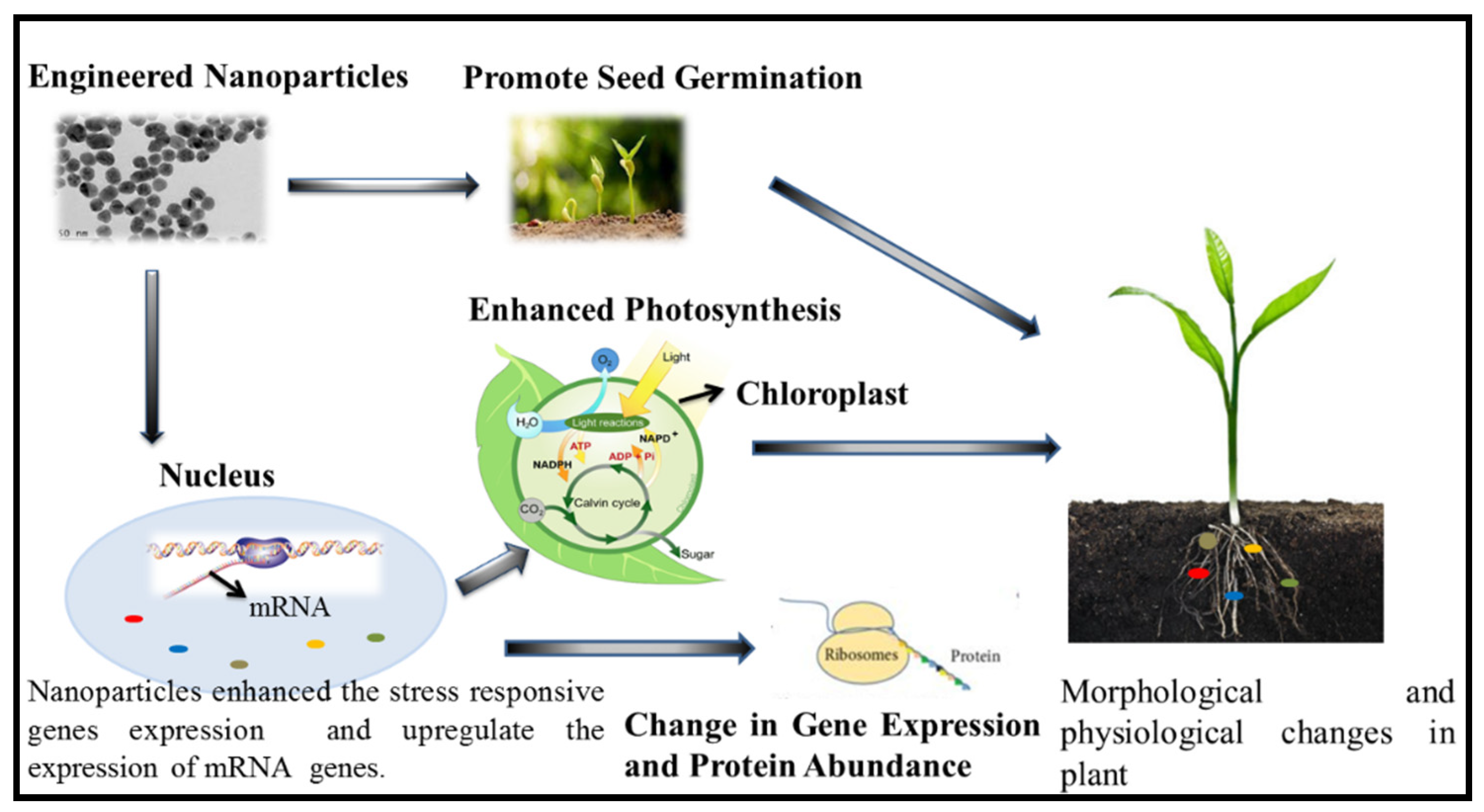
Plants Free Full Text Impact Of Nanomaterials On The Regulation Of Gene Expression And Metabolomics Of Plants Under Salt Stress Html
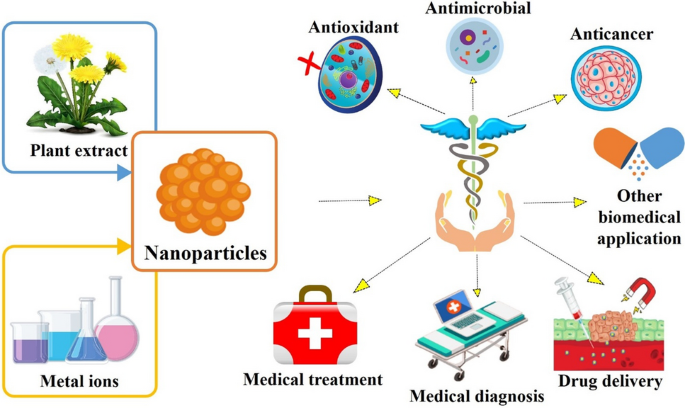
Formation Antimicrobial Activity And Biomedical Performance Of Plant Based Nanoparticles A Review Springerlink
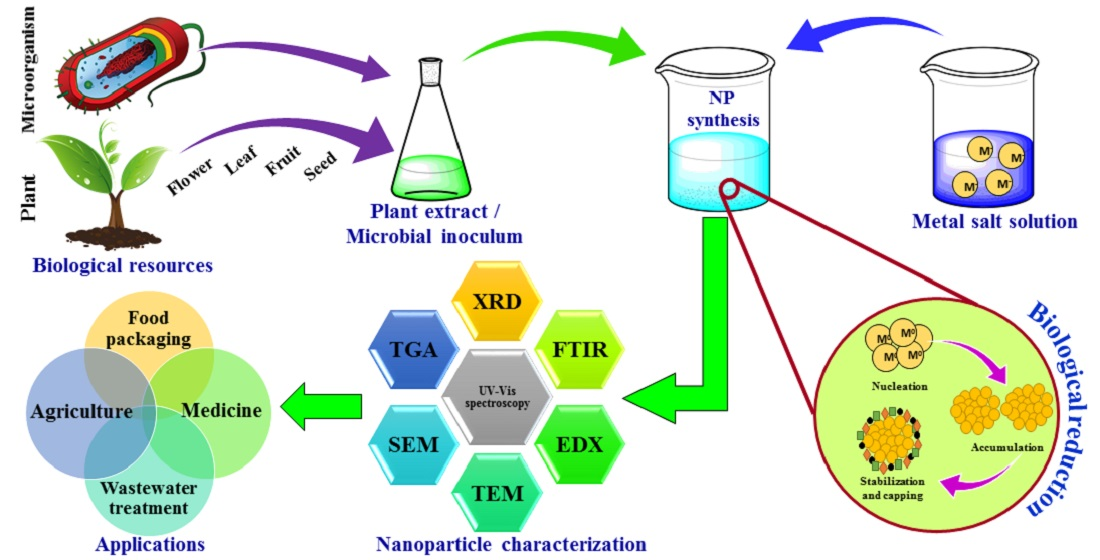
Catalysts Free Full Text Green Synthesis Of Metallic Nanoparticles Applications And Limitations Html

Plant Based Gold Nanoparticles A Comprehensive Review Of The Decade Long Research On Synthesis Mechanistic Aspects And Diverse Applications Sciencedirect
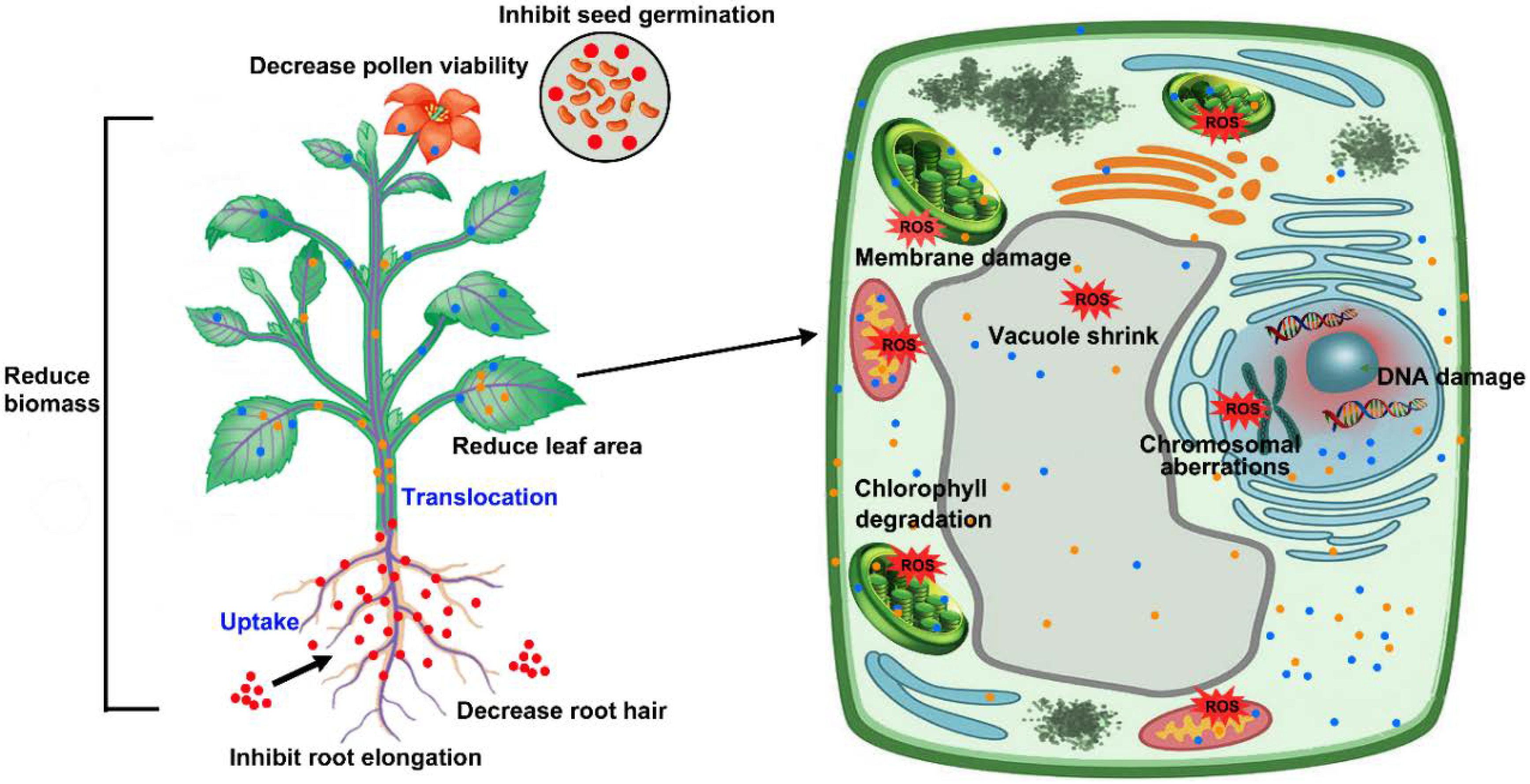
Ijms Free Full Text Impacts Of Silver Nanoparticles On Plants A Focus On The Phytotoxicity And Underlying Mechanism Html

Potential Applications Of Biogenic Selenium Nanoparticles In Alleviating Biotic And Abiotic Stresses In Plants A Comprehensive Insight On The Mechanistic Approach And Future Perspectives
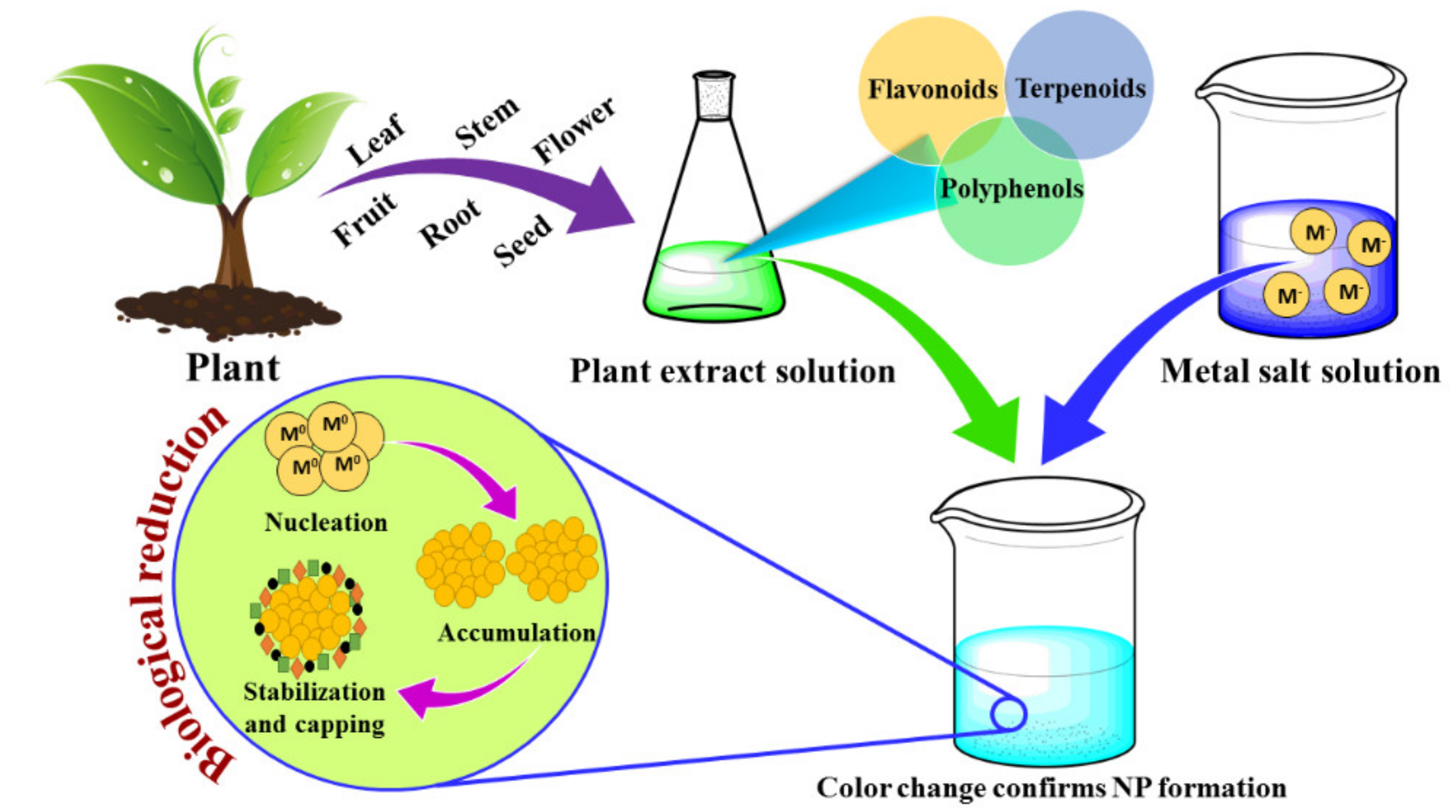
Catalysts Free Full Text Green Synthesis Of Metallic Nanoparticles Applications And Limitations Html

A Review On Plant Extract Based Route For Synthesis Of Cobalt Nanoparticles Photocatalytic Electrochemical Sensing And Antibacterial Applications Sciencedirect
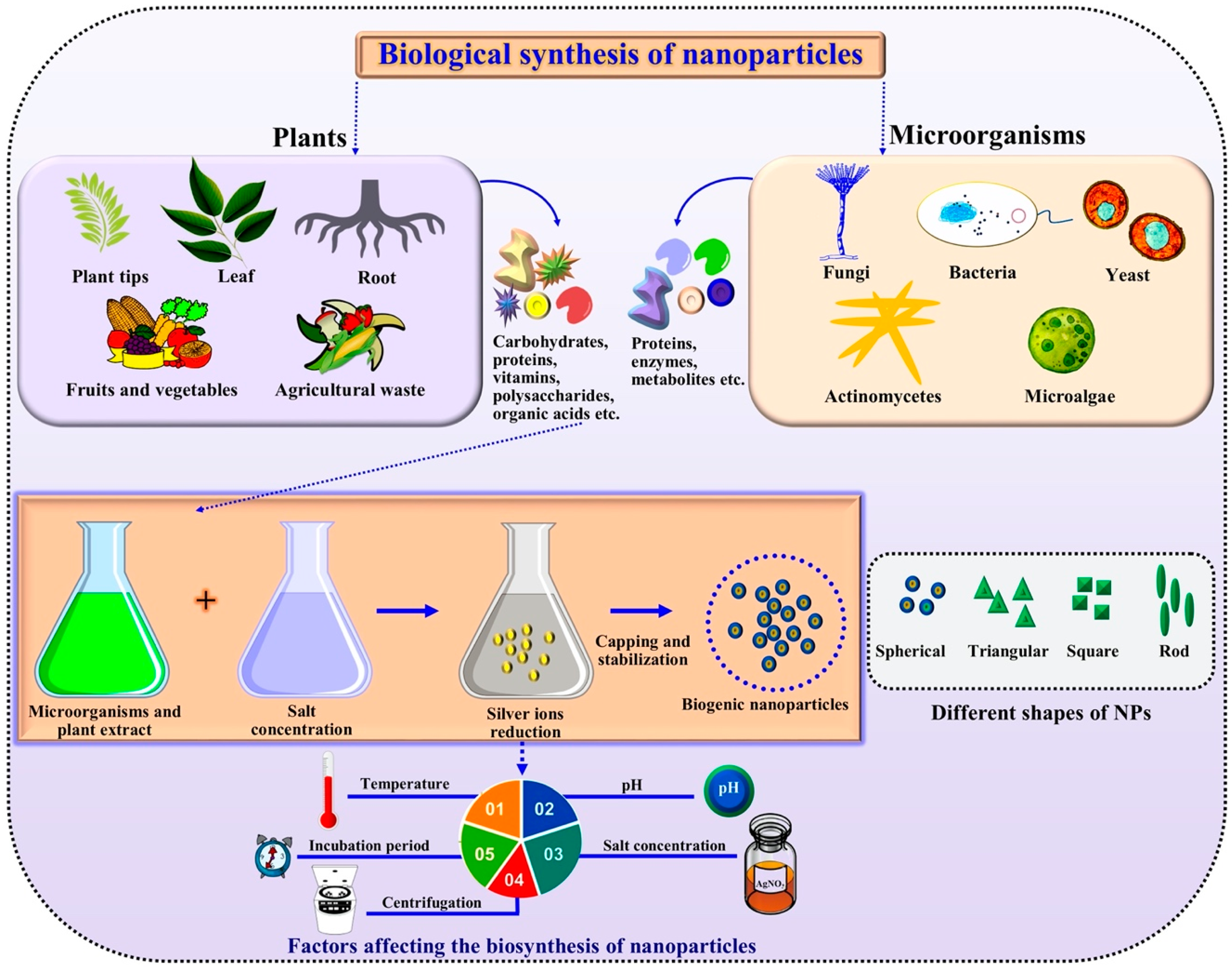
Nanomaterials Free Full Text Advancements In Plant And Microbe Based Synthesis Of Metallic Nanoparticles And Their Antimicrobial Activity Against Plant Pathogens Html
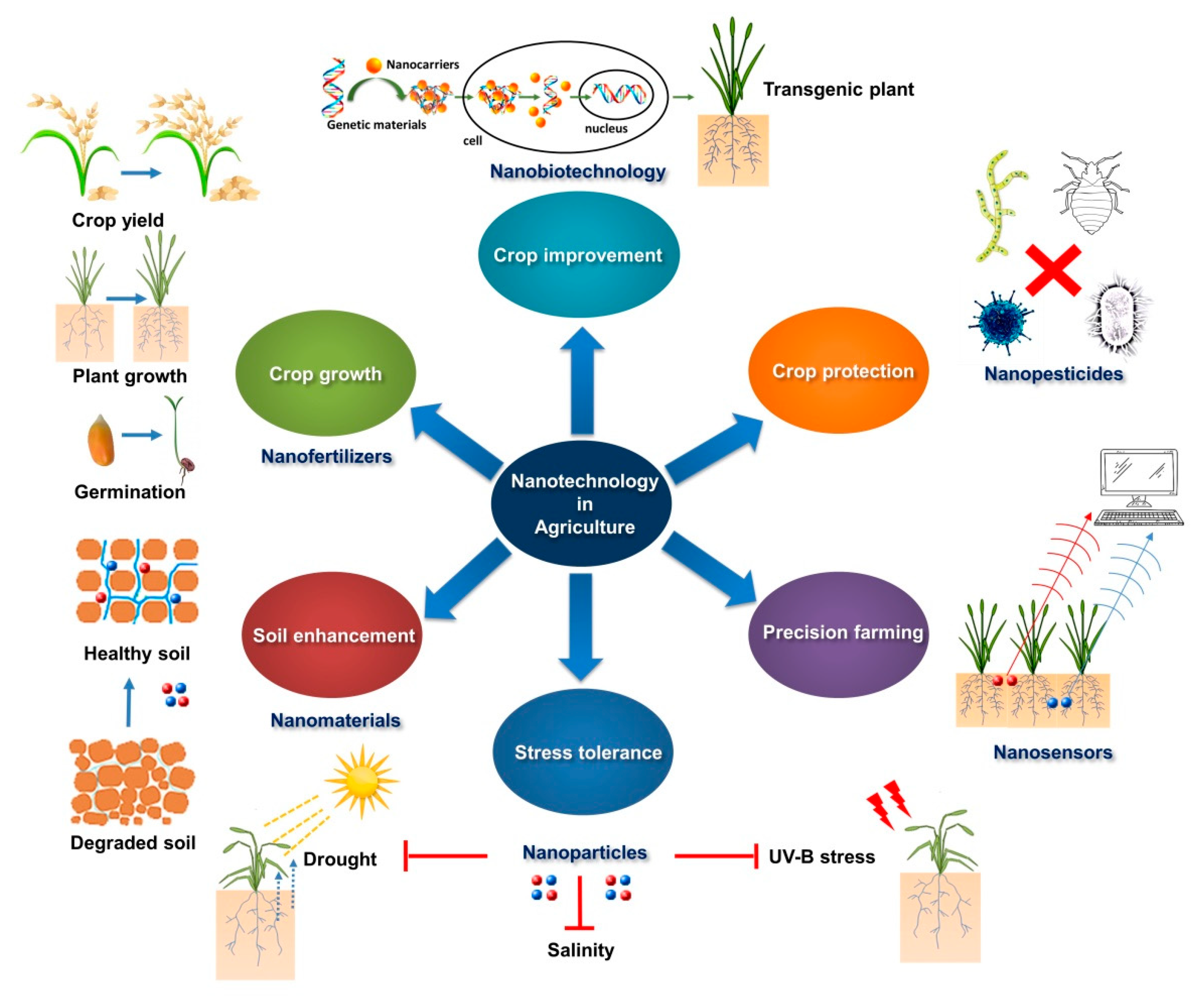
Molecules Free Full Text Applications Of Nanotechnology In Plant Growth And Crop Protection A Review Html

Plant Mediated Green Synthesis Of Metal Based Nanoparticles For Dermopharmaceutical And Cosmetic Applications Sciencedirect
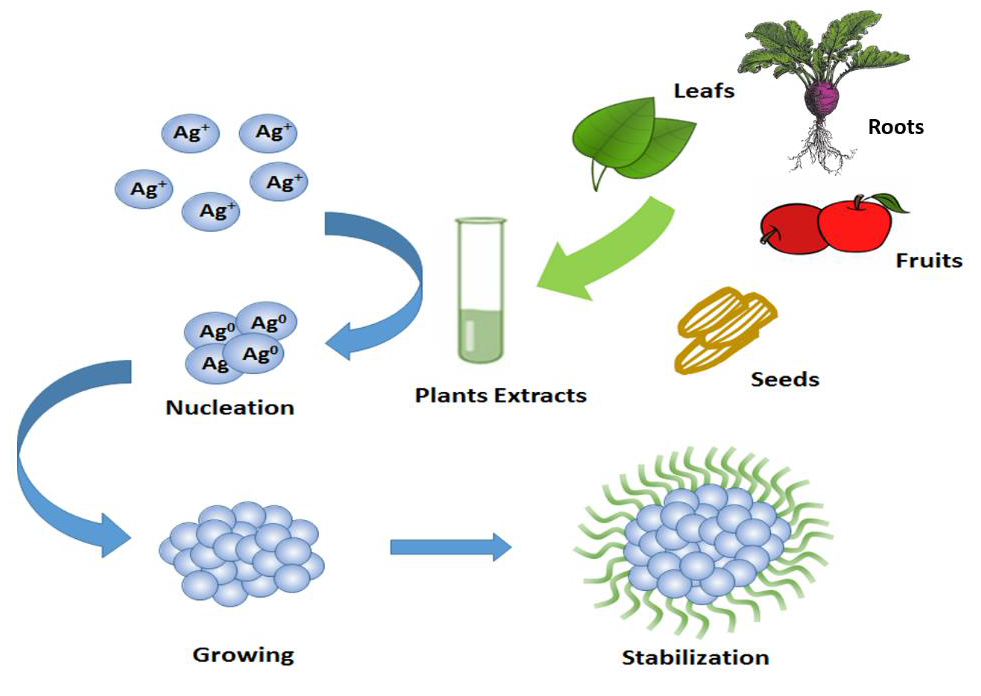
Green Synthesis Of Silver Nanoparticles Using Beetroot Extract

Green Synthesis Of Metal And Metal Oxide Nanoparticles From Plant Leaf Extracts And Their Applications A Review

6 Workflow For Green Synthesis Of Nanoparticles Using Plant Leaf Extract Download Scientific Diagram
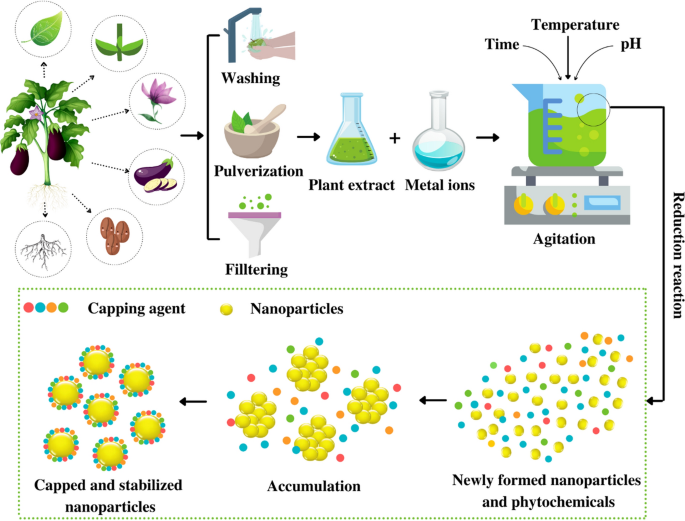
Formation Antimicrobial Activity And Biomedical Performance Of Plant Based Nanoparticles A Review Springerlink
Comments
Post a Comment